다국어 기술된 csv를 import 하는 방법
IMPORTING TRANSLATIONS
As of version 2.6, AtoM will allow you to import new descriptions in multiple languages at once, as a way of adding translations to your source content during an import.
At this time, not all CSV fields support translation imports. Only those fields found in AtoM’s information_object_i18n database table can be imported as translations. These include:
- title
- alternateTitle
- radEdition
- extentAndMedium
- archivalHistory
- acquisition
- scopeAndContent
- appraisal
- accruals
- arrangement
- accessConditions
- reproductionConditions
- physicalCharacteristics
- findingAids
- locationOfOriginals
- locationOfCopies
- relatedUnitsOfDescription
- rules
- sources
- revisionHistory
- institutionIdentifier
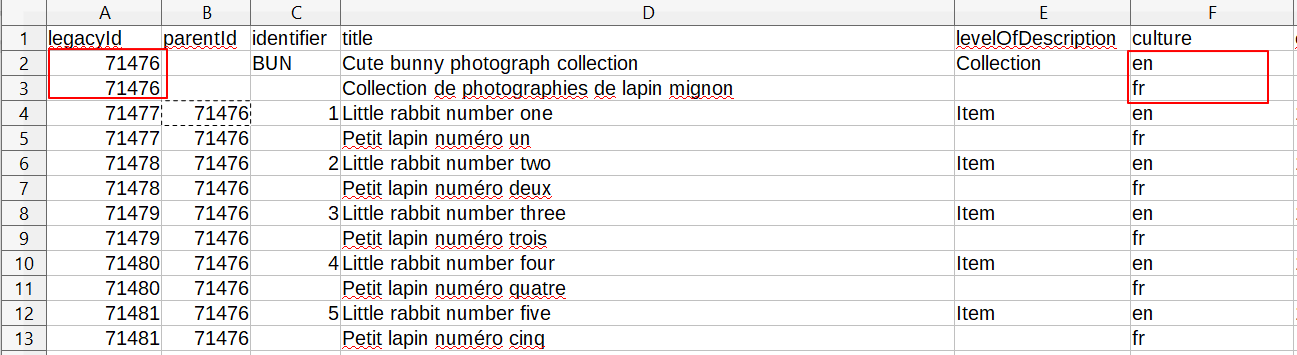
The translation import works on the following logic: whenever AtoM encounters two consecutive CSV rows that have the same legacyId value, but different culture values, AtoM will import the second row as a translation of the first. AtoM expects two-letter ISO 639-1 culture codes to be used in the culture column - e.g. en for English, fr for French, etc. See the section above, Other data entry notes, for further information.
Preparing translations for import
To import new archival descriptions with translations:
- Make sure that every row in your CSV has a
legacyIdand aculturevalue - Place translation rows directly below the source culture row
- Translation rows must have the same
legacyIdvalue as their source culture rows - Translation rows must have a different
culturevalue as their source culture rows - Make sure that all
culturevalues use ISO 639-1 two-letter codes - In the translation rows, leave any columns that do not support translation blank
An example CSV:
Tip
Most fields that can’t currently be translated via CSV import can still be translated via AtoM’s user interface. For more information on translating content via the user interface, see:
Remember that linked entities (such as a creator name, a subject access point, or other terms that are maintained in taxonomies such as the Levels of description, etc) cannot be translated directly on the archival description edit page. Instead, navigate to the linked entity, flip the user interface into the desired translation culture, enter edit mode, add your translation, and save. When you return to your description and view it in the translation culture, the translated entity will now also display in the translation culture.
See also
- CSV validation - LegacyId check

